- Home
-
- TF Integrated Workstation
- TT Integrated Station
- TS Single-Person Station
- TO Single-Person Station
- Advanced Office Table
- Manager Table
- Odette Conference Table
- Lifting White Board
- Lifting Podium
- Working Port
- Zen Standing Desk
- Lifting Coffee Table
- Home Standing Desk
- Nature Standing Desk
- Invictus Gaming Desk
- Study Desk
-
-
- Electric Hospital Bed
- Image Equipment
- Examination Bed/Clinic Bed
- Operation Table and Chair
- Infant Incubator
- Independent Weighing System
- Home Care Bed
- Patient Lift
- Wheelchair
- Toilet Lift
- Bath Lift
- Shower Trolley
- Smart Rollator
- Ophthalmic Workstation
- Treatment Chair
- Facial Chair
- Traction Table
- Massage Chair
- OT Training Equipment
- Stand-up Application
- Rehabilitation Robot
-
-
- Photovoltaic Application
- Photothermal Application
- Energy Storage Container
- Tractor
- Seeder
- Fertilizer Spreader
- Harvester
- Rotary Cultivator
- Climate Control System
- Automatic Feeding System
- Excavator
- High Altitude Work Platform
- Garbage Truck
- Street Sweeper
- AMR Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) and Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR)
- Forklift Accessories
- Palletizing Collaborative Robots
- Packaging Machine
- Mobile Light Tower
-
-
Industrial Linear Actuator Working Principle and Key Components Detailed Guide
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-10 Origin: Site
In the field of industrial automation, industrial linear actuators play a vital role in converting energy into precise linear motion. From adjusting machine parts to opening valves or lifting heavy objects, these devices are essential for smooth and efficient operation.
Whether in machinery, robots or precision control systems, industrial linear actuators provide the motion required to accurately and reliably automate repetitive tasks. With the rapid advancement of technology, new actuators such as radio remote control actuators and magnetic linear actuators are becoming increasingly popular due to their versatility and low maintenance. This guide will explore what you need to know about industrial linear actuators, including linear actuator working principle, types and key components.
1. What is an Industrial Linear Actuator?
An industrial linear actuator is a mechanical device used to move loads in a straight line. It uses mechanisms such as screws, belts or magnetic fields to convert rotary motion (usually from a motor) into linear motion.
The main applications of industrial linear actuators include:
Manufacturing: for machine positioning and conveyor automation
Agriculture: for automatic feeding, irrigation and harvesting equipment
Aerospace: for controlling flaps, landing gear or cabin functions
Medical equipment: for hospital beds, dental chairs and diagnostic equipment
Construction equipment: for heavy lifting and material handling systems
These industrial linear actuators help reduce manual labor, improve precision and ensure consistent performance in mission-critical applications.
2. How does a Linear Actuator Work?
To understand how a linear actuator works and the types of industrial linear actuators, you need to understand their basic motion conversion mechanism.
Industrial linear actuator types step by step working principle:
1. Power input: Depending on the actuator type, electricity, fluid pressure or air can be used.
2. Rotary motion generation: A motor or piston generates rotational force.
3. Conversion to linear motion: A mechanism such as a lead screw or piston converts the rotational force into linear motion.
4. Output motion: The actuator extends and retracts to move the connected load.
Differences between different types of industrial linear actuators:
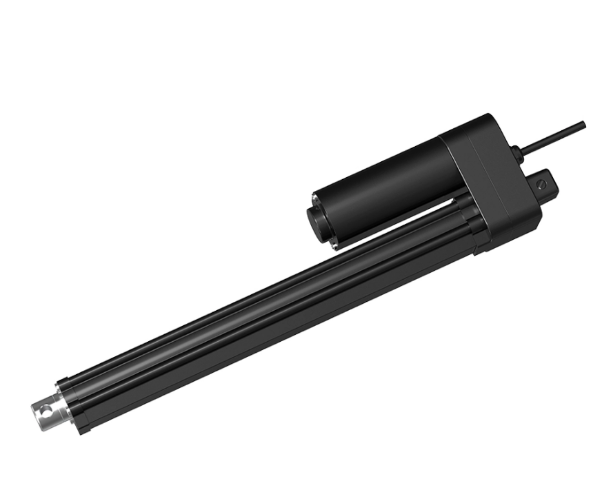

Electric linear actuators: Use motors and gears to achieve controlled, programmable motion, such as industrial linear actuator JC35FA21, JC35SA22 .
Hydraulic actuators: Utilize pressurized fluids for high-force applications, but require pumps and hoses.
Pneumatic actuators: Use compressed air and are best suited for fast, light movement.
Each type offers unique advantages based on speed, force, and environmental limitations.
3. Common Industrial Linear Actuator Types
Understanding the various industrial linear actuator types can help you choose the actuator that best suits your application.
Radio controlled actuator
Most common in automation; precise, clean, low maintenance;; suitable for programmable motion control.
Hydraulic linear actuator
Heavy duty linear actuators suitable for heavy-duty tasks; high output force, but there may be fluid leakage; requires regular maintenance.

Pneumatic linear actuator
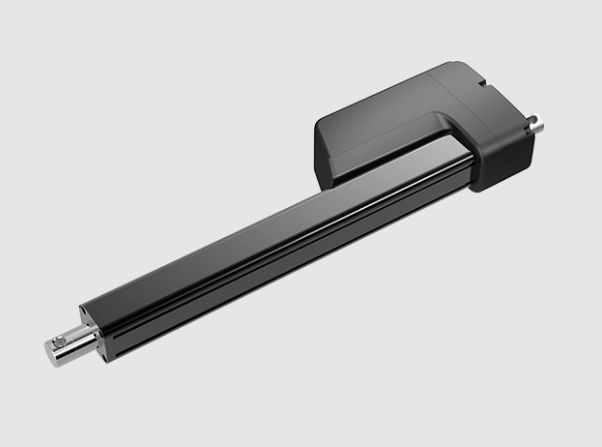
Fast and cost-effective; ideal for repetitive tasks; best for use in environments with compressed air, such as linear actuator JC35FA17.
Magnetic linear actuator
Non-direct contact operation, reducing friction and wear; ideal for clean rooms, laboratories or low-contamination environments; provides high-speed and smooth movement.
Radio remote control actuator
Wireless control via RF signals; ideal for hard-to-reach or mobile equipment; widely used in smart factories and remote applications
4.Industrial Linear Actuator Parts
Industrial linear actuators are made up of several key linear actuator parts, each of which plays an important role in its function:
Motor: drive system - can be AC, DC or stepper motor
Gearbox: adjusts speed and torque to the desired level
Screw/ball screw: converts rotary motion to linear motion
Housing: protects internal components and ensures structural integrity
Feedback sensor (optional): measures position or speed for closed-loop control
These linear actuators Together, the parts ensure that the actuator operates efficiently and meets the needs of a specific application.
5. Position Feedback and Control Systems
Lots of applications require linear actuators with position feedback to improve accuracy and safety.
Feedback methods include:
(1) Potentiometers: Cost-effective analog position tracking
(2) Hall effect sensors: Detect magnetic fields for durable and reliable feedback
(3) Encoders: Provide high-resolution digital signals for precise control
These linear actuators with position feedback systems support closed-loop control, allowing the actuator to adjust in real time based on sensor input—ideal for robots, CNC machines, and automated inspection systems.
6. Selecting the Right Industrial Linear Actuator
When selecting a linear actuator, consider the following key factors:
Load capacity: Make sure it can withstand the required forces
Stroke length: Match the linear stroke to the application requirements
Speed requirements: Select based on motion timing
Control method: Analog, digital, or remote control via PLC integration
Environmental conditions: Dust, moisture, vibration, or temperature

Magnetic linear actuators are suitable for environments that require low wear and high cleanliness. Radio controlled actuators are best suited for most automation devices.
Integration with a PLC system or IoT-enabled controller can enhance the actuator's responsiveness and system efficiency.
7. Future Trends and Innovations
Industrial linear actuators are developing rapidly, such as:
IoT integration: actuators that transmit performance data to a central system for predictive maintenance.
AI-based control: intelligent motion adjustments based on real-time environmental feedback.
Energy-saving design: reducing power consumption while maintaining torque and speed.
Wireless and radio control: radio-controlled actuators are increasingly used in mobile robots and smart factory production lines.
Conclusion
Choosing the right industrial linear actuator can significantly improve productivity, precision, and operational reliability. By understanding its types, working principles, and key components, you can ensure better design, integration, and maintenance of your system.
Whether you are looking for a magnetic linear actuator for cleanrooms or a radio controlled actuator for wireless automation, this guide can provide you with a solid foundation.
The JIECANG linear drive product platform not only provides automation for industrial linear actuators, but also provides intelligent control solutions for medical industries such as wheelchairs and electric medical beds, as well as smart home fields such as adjustable bed frames.
Industrial Linear Actuator FAQs:
1. What is an industrial linear actuator used for?
An industrial linear actuator is used to create straight-line motion in machinery. Common applications include machine automation, robotics, conveyor systems, valve control, and lifting mechanisms in industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and aerospace.
2. When should I use a magnetic linear actuator?
Magnetic linear actuators are ideal for applications that require low maintenance, minimal friction, and operation in clean or contamination-sensitive environments, such as laboratories or medical equipment.
3. Are radio-controlled actuators reliable for industrial use?
Yes, radio-controlled actuators are increasingly used in industrial environments for their convenience in remote or hard-to-access applications. They are reliable when paired with robust control systems and secure communication protocols.
Related Articles
QUICK LINKS






























